Publication in the American Journal of Hematology - scientists from the IIMCB discovered new 'sensors' for iron levels in the body
Researchers from the International Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology in Warsaw (IIMCB) have achieved success: a scientific paper describing the latest discoveries in the field of iron metabolism has been published in the prestigious American Journal of Hematology. The research results may have applications in medicine and lead to new therapies.
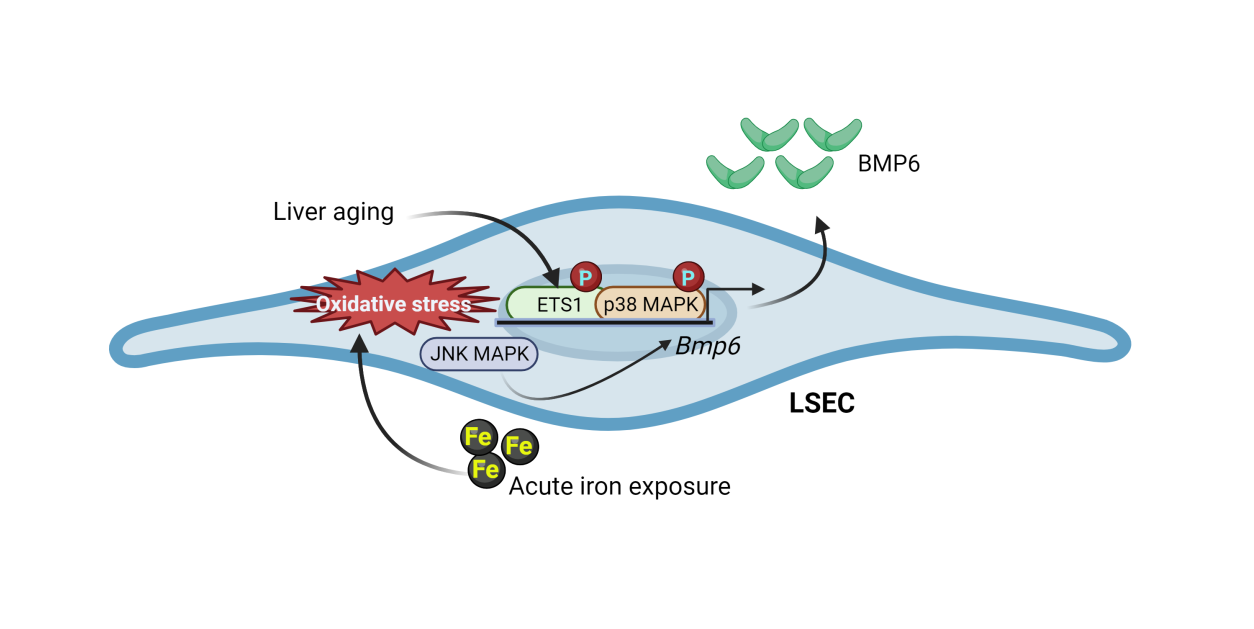
Gabriela Żurawska and the team from the Laboratory of Iron Homeostasis, led by Katarzyna Mleczko-Sanecka, are the authors of the article "Iron-triggered signaling via ETS1 and the p38/JNK MAPK pathway regulates Bmp6 expression". Iron deficiency is a global health problem - it is estimated to affect at least a billion people worldwide[1]. Iron is a trace element essential for many vital functions, but both deficiency and excess of iron can be harmful, leading to organ damage and the development of diseases. Therefore, as the researchers argue, the level of iron in the body should be strictly controlled.
Surprisingly, it was only in the last two decades that the molecular mechanisms controlling iron levels in the human body were discovered. A small hormone produced by the liver, called hepcidin, was described as a key regulator of systemic iron homeostasis. Subsequently, scientists identified another protein, the cytokine BMP6, which activates hepcidin production. BMP6 acts as an 'iron sensor' – the synthesis of this protein increases with excess iron in the body. However, the molecular mechanisms responsible for the regulation of BMP6 by iron levels in the body are still poorly understood.
Scientists from the International Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology in Warsaw discovered a new cellular signaling pathway that induces BMP6 under conditions of iron excess, consisting of MAP kinases and a factor called ETS1. The researchers showed that these proteins are activated by free radicals generated by iron accumulation and directly bind to DNA to induce increased BMP6 expression. This discovery may pave the way for new therapies aimed at correcting iron balance by modulating BMP6 levels and potentially help diagnose the genetic basis of iron metabolism disorders of previously unknown cause.
The scientific article titled "Iron-triggered signaling via ETS1 and the p38/JNK MAPK pathway regulates Bmp6 expression" in the American Journal of Hematology was created under the direction of researchers from IIMCB: Gabriela Żurawska as the first author and Katarzyna Mleczko-Sanecka as the corresponding author, with the participation of researchers from the Maria Sklodowska-Curie National Research Institute of Oncology, the Mossakowski Medical Research Institute of the Polish Academy of Sciences, the Medical University of Warsaw, and the Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology of the Polish Academy of Sciences.
The publication is available at the link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ajh.27223
[1]https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/133/1/30/6613/Iron-deficiency