Nucleic acid-based therapeutics
Antisense technology is an emerging therapeutic approach for inhibiting gene expression through recognition and RNase H1-dependent degradation of cellular mRNAs. In this technology, short, synthetic, single-stranded oligonucleotides (ASOs) are designed that are complementary to the target mRNA.
ASOs are frequently chemically modified for enhancing the therapeutic properties of these molecules. The most widely used modifications include phosphorothioate (PS) backbone and modifications of the sugar moieties at 2’ site. The molecular mechanism of toxicity of chemically modified antisense oligonucleotides are not fully understood.
Hyjek-Składanowska M, Vickers T, Napiórkowska A, Anderson BA, Tanowitz M, Crooke ST, Liang X, Seth PP&, Nowotny M&. Origins of the increased affinity of phosphorothioate-modified therapeutic nucleic acids for proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142 (16): 7456-7468;
& - corresponding authors
-
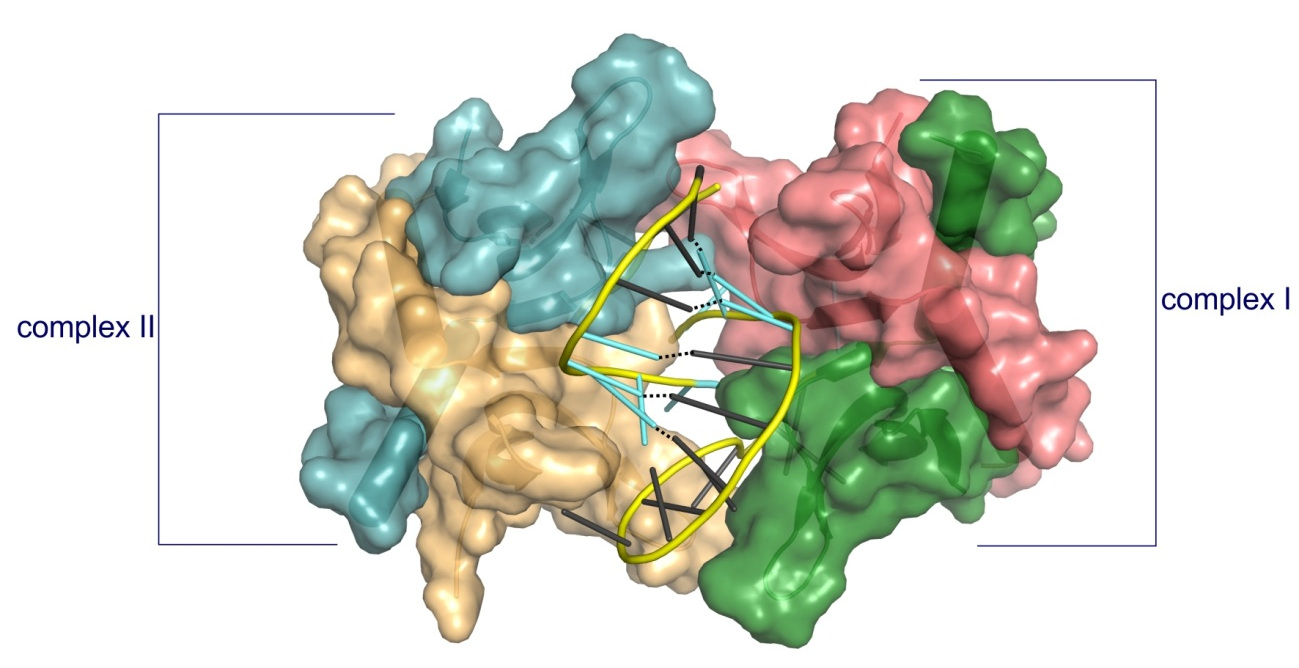
The first crystal structure of a complex between a protein and fully PS nucleic acid (DNA-binding domain of a model ASO-binding protein PC4 in complex with full PS 2′-OMe DNA gapmer ASO).
-
The structure reveals a possible mechanism of ASO-induced toxic protein aggregation: ASO is bound in hairpin-like conformation and its exposed gapmer part promotes the formation of a dimer of dimers of PC4 through base pairing.
-
The protein interacts with the PS-nucleic acid through a network of electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. Importantly, the backbone of the PS ASO is able to form new and more extensive hydrophobic interactions than a natural phosphodiester backbone which provides insights into the origins for the enhanced affinity of PS for proteins.
The studies of PC4-ASO complex have been performed in cooperation with Ionis Pharmaceuticals (Carlsbad, California, USA).
Structure of PC4 in complex with PS 2′-OMe DNA gapmer ASO. The content of the asymmetric unit of the PTEN ASO complex crystal. PC4 protomers are color-coded and shown in surface representation, DNA is shown in cartoon (PS backbone is shown in yellow, 2′-OMe PS nucleotides are shown in aquamarine, DNA gapmer nucleotides are shown in dark gray). The base pairing between the nucleotides is shown as black dotted lines.
Hyjek-Składanowska M, Anderson BA, Mykhaylyk V, Orr C, Wagner A, Poznański JT, Skowronek K, Seth PP, Nowotny M. Structures of annexin A2-PS DNA complexes show dominance of hydrophobic interactions in phosphorothioate binding. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022;, gkac774, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac774
-
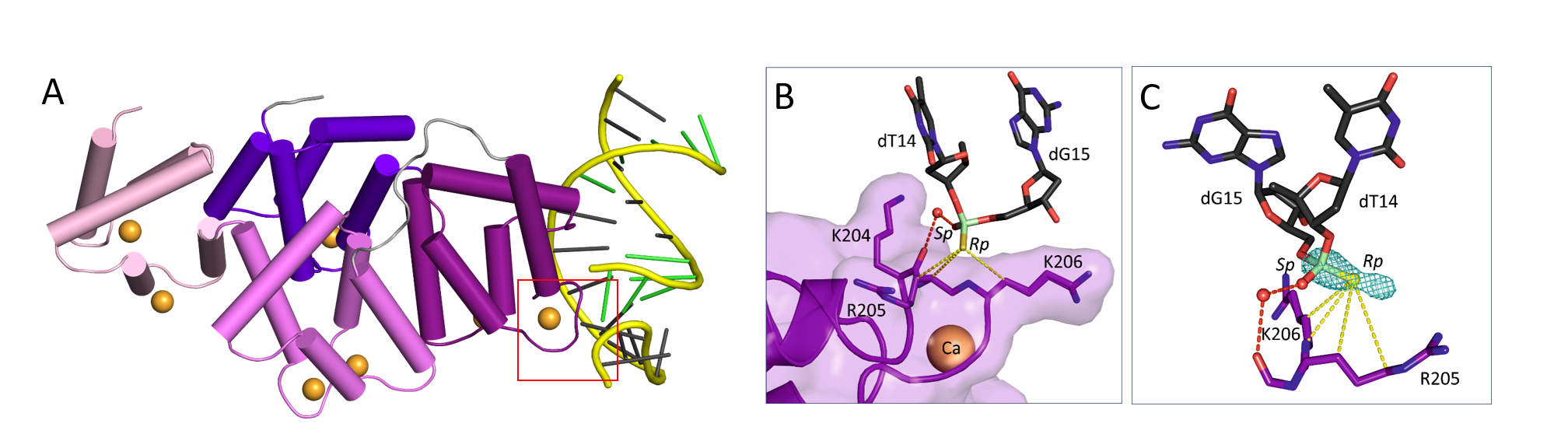
The first crystal structure of a complex between a PS oligonucleotide and non-specific nucleic acids binding protein (core domain of annexin A2).
-
Interactions between the sulfur atom of the PS linkage and the protein surface are mainly of hydrophobic character - the hydrophobic nature of sulfur contributes to the association of PS ASOs with proteins.
-
Measurements of anomalous diffraction of sulfur confirmed that van der Waals contacts between the sulfur atom and hydrophobic parts of arginine and lysine side chains drive the enhanced interaction of PS ASOs with proteins.
-
Stereoisomer preference at given phosphorothioate in the DNA oligonucleotide is determined by the environment around the PS linkage coming from the protein and other adjacent structural features such as 5-Me groups on cytosine nucleobases.
The studies of AnxA2-ASO complex have been performed in cooperation with Ionis Pharmaceuticals (Carlsbad, California, USA) and Diamond synchrotron (Didcot, Oxfordshire, UK).
(A) Crystal structure of AnxA2 in complex with PS ASO duplex. Calcium-binding annexing domain I-IV are coloured light pink, violet, purple, and purple blue, respectively. Calcium ions are shown as orange spheres. DNA is shown in cartoon (PS backbone is shown in yellow, 2’-MOE PS nucleotides are shown in green, DNA gapmer nucleotides are shown in dark gray). (B) Close-up view on the phosphorothioate-binding surface in AnxA2. Polar interactions are shown as red dotted lines. Van der Waals interactions are shown as yellow dotted lines. (C) Difference Fourier anomalous map calculated based on long-wavelength X-ray diffraction data (λ = 2.7552 Ȧ), shown as teal mesh. The preferred occupancy of Rp PS stereoisomer is facilitated by the hydrophobic interactions with surrounding amino acids.